Home » Press Bulletin and Blog » 10 Questions About DRC

- What is the difference between natural and lab-grown diamonds?
Natural diamonds and lab-grown diamonds cannot be distinguished by the naked eye. Small amounts of nitrogen are present in natural diamonds, however, nitrogen is absent from lab-grown diamonds. This is indeed one of the indicators that gemologists look for when determining whether a diamond is man-made or natural.
Natural diamonds are formed throughout millions of years under the pressure of the earth’s crust, after which they are mined, cut, and polished. The same tests are run on a lab-grown diamond but in a different setting. The method employed to produce a Lab Grown Diamond drastically reduces the growth period, from millions of years to a few months. The Lab Diamond is then polished and cut. The majority of natural diamonds contain trace amounts of other compounds, especially nitrogen, which gives them a yellow tint, or (rarely) boron which gives them a blue colour.
Lab-grown diamonds—also referred to as man-made or synthetic diamonds—began to be sold in large quantities on the gem and jewellery market. Although they look just like natural diamonds, they have extremely slight variances that can only be found by skilled gemologists using specialized equipment.
2. How do we identify whether the diamond is mined or lab-grown?
The majority of lab-grown diamonds are ethically and openly acknowledged as being man-made, which is the first thing to recognize. Non-disclosed lab-grown diamonds that are being marketed as natural diamonds are the biggest concern in the jewellery sector. However, it’s crucial to be aware that the majority of companies producing lab-grown diamonds are entirely genuine and sincere businesses that are forthright about their goods. To properly identify their diamonds as lab-grown, some even laser inscribe all of them. Whatever the situation, tests may be performed to identify whether the diamond is natural or man-made.
Traditional gemological observations and outdated “diamond detectors” are unable to distinguish laboratory-grown diamonds from their natural counterparts since they are virtually, chemically and optically identical to them. They can only be distinguished from genuine diamonds through identification at a reputable gemological laboratory or by using high-tech tools created by DRC and other organizations.
Type IIa test
UV radiation test
Here are machines that help in detecting lab-grown diamonds
J-MINI-PRO: https://drcindia.in/products/j-mini-pro-diamond-detection/
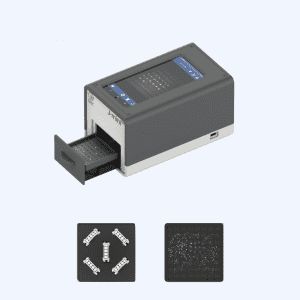
J-SMART-PRO: https://drcindia.in/products/j-smart-pro-diamond-detection/

J-DETECT-PRO: https://drcindia.in/products/j-detect-pro-diamond-detection/

3) What is DRC?
DRC is a technology and innovation firm that provides clever and affordable techno-commercial solutions. With care and innovation at our core, we are now world leaders and a well-known name in lab-grown (CVD/HPHT) diamond detection technology. We assist and enhance the diamond industry at every level of the supply chain, from production to retail, by offering affordable, high-value solutions, business innovation, and effective customer service. Our tried-and-true solutions have reduced human error, increased productivity, and allowed customers to make secure and informed purchases for thousands of happy customers.

4) What does DRC aim to do?
Our purpose and goal are to benefit society as a whole by providing creative, cost-effective technological solutions to challenges in a variety of sectors.
5) Which products of DRC offer what? How do the products work?
The products of DRC offer low downtime, high-cost efficiency & continual production.
DRC has various products which serve the purpose of diamond detection, identification to diamond photography. Here’s a summary of what each product is barely used for.
| Product Name | Purpose of the product | What does the product do? |
| D-imaging | Photography of diamond | They provide a 2x faster ultra-rapid photography solution to increase production simultaneously. |
| D-craft | Diamond auto polishing | D-craft is an auto-polishing technology that crafts the full pavilion and 8 facets in the crown of a diamond. It has automatic weight control technology which prevents the burning of the stone, cutting the diamond consistently alongside maintaining its symmetry and avoiding unnecessary weight loss |
| J mini pro | Diamond detection | The J series is the ‘diamond detectors’. They help the gemologists know whether the diamonds are natural or lab-grown. |
| J smart pro | Diamond detection | Tests the diamonds of all shapes, sizes, and colours to classify or identify their type (to know whether they are natural/mined or lab-grown) |
| J-detect pro | Diamond detection | They help the gemologist understand the type of diamond they are running the test for. It sets a clear distinction between lab-grown and mined diamonds. Thus, making the ‘identification’ process easier. |
| GemID | Diamond DNA identification | It captures the digital footprint of the diamond scanned (thus identifying the DNA of the diamond) which is like giving the diamond the unique identification it requires. |
To know the working of the product, you can refer to the product specifications and details on our website. We also have detailed blogs on each product where you will find all the information in one place.
6) How do I know which product of DRC I need for my use?
Each product of DRC serves a different purpose. First, list down your needs. What are your requirements for the product? Only after you are clear with the purpose of your product purchase, can you pick the perfect product. After setting your needs, see the product features of each product on our website by clicking the following link.
Here, we have mentioned in short, the features and purpose each product serves. If any product interests you, click on the Explore Now button to read the product specification in detail.
7) Is it true that diamonds never break?
It’s simple to believe that diamonds are unbeatable because of their superior hardness and stability. Every gem, however, has its weaknesses. Diamonds can thus break, sure. The good thing is that it happens so infrequently.
Most individuals wear and destroy their pricey diamond jewellery without even realizing it. The majority of them break into sharp points or tiny chips. Atoms are not strongly bound in these regions. Diamonds do not break when dropped, although they can be chipped by strong, unintentional strikes.
They may also crack if a condition known as “strain” causes pressure to build up inside the stone. Small taps cause breaking, allowing the pressure to release. Although it is quite uncommon for diamonds to shatter in this fashion, it is a truth to be aware of.
8) How are diamonds formed (naturally)?
Simply explained, diamond creation happens when the earth’s deep carbon deposits—located between 90 and 125 miles below the surface—are exposed to extreme heat and pressure. While some stones take millions of years to form, others do it in a matter of days or months. When it comes to coloured diamonds, interactions between trace elements during the diamond’s development are what give them their hue. Additionally, it is very hard to pinpoint a diamond’s exact age, although geologists can make an educated guess thanks to the existence of certain minerals.
9) How are diamonds created in a lab?
Laboratory-made diamonds are created in an artificial setting that replicates the natural creation of diamonds below the Earth’s mantle. There are two methods used to create lab diamonds: CVD (chemical vapour deposition) and HPHT (high-pressure high temperature).
The processes include a tiny piece of the diamond being put into a chamber, where it is heated to an extreme temperature and exposed to a carbon-rich gas. The carbon gas ionises over just a few weeks, causing the particles to adhere to the original diamond slice before eventually crystallising into a whole diamond.
The most common technique for making lab diamonds is CVD. The procedure is speedier, less expensive, and requires less energy for production. A relatively flawless slice of diamonds can be chosen for growth during CVD, whereas HPHT is more likely to fail if a diamond with internal flaws is initially used; the diamond can explode or pick up more inclusions as it grows.
10) How accurate are your machines?
Here’s a summary of statistics showing the accuracy of our products.
| Product name | Level of accuracy |
| D-craft | Accurate final polishing as per the planning parameter. (EX: Cutting and VG+ = Polishing) |
| J mini pro | 98%+ |
| J smart pro | 98%+ |
| J detect pro | 98%+ |
| GemID | Register DNA while it’s a loose diamond and recognize it even after it is studded. |
Visit our website: https://drcindia.in/
Stay connected with us to learn more tips and tricks. All you have to do is follow us here:
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/DRCPVTLTD
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/drcpvtltd/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@DRCIndia



